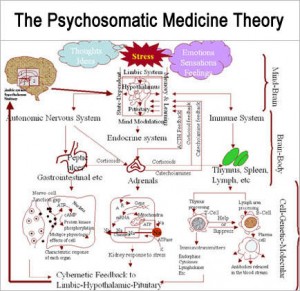
Psychosomatic medicine focuses on the interactions between mind and body and the powerful ways in which emotional, mental, social and spiritual factors can directly affect health.
Psychosomatic medicine focuses on the study and treatment of those emotional disturbances that are manifested as physical disorders. The term psychosomatic emphasizes essential unity of the psyche and the soma, a combination rooted in ancient Greek medicine. Common disorders caused at least partly by psychological factors include childhood asthma, certain gastrointestinal problems, hypertension, endocrine disturbances, diabetes, and possibly even heart disease.
Psychosomatic medicine deals with:
- Clinical situations where mental processes act as a major factor affecting medical outcomes.
- illnesses due to the interaction of the mind and the body
- physical diseases which have a mental component derived from the stresses and strains of everyday living ex. lower back pain, high blood pressure
- the influence that the mind has over physical processes
- disabilities that are based on intellectual infirmities, rather than actual injuries or physical limitations, (somatoform disorders)
- physical illness with their biopsychosocial aspects e.g. cancer diseases
- physiological and functional disorders as response to psychological or physical trauma e.g. posttraumatic stress disorder and adjustment disorders
- Conversion disorders physical symptoms , which go back to unconscious conflicts
- Hypochondria
- disturbed health behavior and its consequences (e.g. smoking)
- mental disorders associated with physical discomfort: depression, anxiety disorders
- mental illness, which have physiological effects : eating disorders, personality disorders
Psychosomatic medicine treatments are necessary in 3 different situations:
- The patients who have both a mental (psychiatric) illness and a medical illness, and these illnesses complicate the symptoms and management of each other
- The patients who have a psychiatric problem that is a direct result of a medical illness or its treatment, such as having depression due to cancer and its treatment.
- Somatoform disorders. Somatoform disorders are psychiatric disorders that are displayed through physical problems. In other words, the physical symptoms people experience are related to psychological factors rather than a medical cause.
Some examples:
- Conversion disorder
- Somatization disorder
- Hypochondriasis
- Body dysmorphic disorder
- Pain disorder
Treatment types
- psychotherapeutic conversation
- dynamical psychotherapy
- psychoanalyze
- analytical group therapy
- family therapy
- suggestive therapy
- hypnosis
- body centered therapy
- self-help groups
Advantages of residency training in psychosomatic medicine
Psychosomatic medicine and Psychotherapy is an exciting and new growing medical specialty with a fast and constant evolution. It offers a new point of view regarding the correlation between physical and (somatic) illness and psychiatric factors that create somatic illnesses without physical substance. An interesting aspect is the fact that a psychosomatic medicine and Psychotherapy practitioner has the opportunity to conduct psychiatric evaluations and treatments for mentally healthy individuals without having to interact with common psychiatric patients.
In Germany psychosomatic primary care is compulsory part of training in all specialties. All practicing physicians need to complete an 80-hour course of basic psychosomatic care (psychosocial diagnostic interview, psychotherapeutic interventions, and relaxation techniques). The most common training method in psychosomatic medicine is based on the Balint groups method, in which a group of doctors, therapists and Psychologists consult with each other regarding the treatments of the patients and the treatment relationships.
The residency training lasts 5 years and the required rotations are the following:
- 1 year psychiatry and psychotherapy (6 months can be spent in the department of child and adolescent psychiatry)
- 1 year Internal medicine
- 3 years in psychosomatics
If you start a residency in psychosomatic medicine and want to change your specialty, you can get some part of your residency training in psychosomatic medicine recognized in the following specialties:
- Anesthesiology – 12 Months
- Surgery – 6 Months
- Gynecology – 6 Months (training in psychosomatics is mandatory)
- Human genetics – 12 Months
- Internal medicine and general medicine – 12 Months (training in psychosomatics is mandatory)
- Pediatrics and adolescent medicine – 6 Months
- Child and adolescent psychiatry and psychotherapy – 12 Months
- Neurology – 12 Months
- Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation
- Psychiatry -12 Months
- Pathology – 12 Months
- Pharmacology – 12 Months
- Radiology – 12 Months
Supra specialties of psychosomatic medicine are:
- Psychoanalysis
- Psychotherapy
- Rehabilitations medicine
- Acupuncture
- Allergology
- Occupational medicine
- Geriatrics
- Homeopathy